If you have a SaaS product, you know how much effort goes into creating something people love.
However, getting it seen by the right audience? That’s a whole different challenge.
SaaS platforms have dynamic content, multi-step user journeys, and longer sales cycles, unlike regular websites.
Translation? Traditional SEO strategies just won’t cut it.
And get this: over 68% of SaaS website traffic comes from organic search. [Source: B2B SaaS SEO Statistics for 2024 | Powered by Search]
That’s a huge chunk of potential customers you could be missing without the right foundation.
So, here is a Technical SEO Checklist for your next SaaS product launch:
| Category | Checklist Item |
| Pre-Launch SEO Strategy | Keyword Mapping |
| SEO-friendly URL Structure | |
| Meta Tags Setup | |
| Analytics & Tracking Setup | |
| Core Web Vitals & Speed | LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) |
| FID (First Input Delay) | |
| CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) | |
| Image & Asset Optimization | |
| Sitemap & Robots.txt Setup | Create XML Sitemap |
| Submit Sitemap in GSC | |
| Configure Robots.txt | |
| Schema & Structured Data | Add Organization Schema |
| Add Product or SaaS Schema | |
| Implement FAQ Schema | |
| Validate Scheme | |
| Crawl & Indexation | Test Key Pages with URL Inspection Tool |
| Set Canonical Tags | |
| Noindex Low-Value Pages | |
| Internal Linking Ready | |
| Mobile Usability Testing |
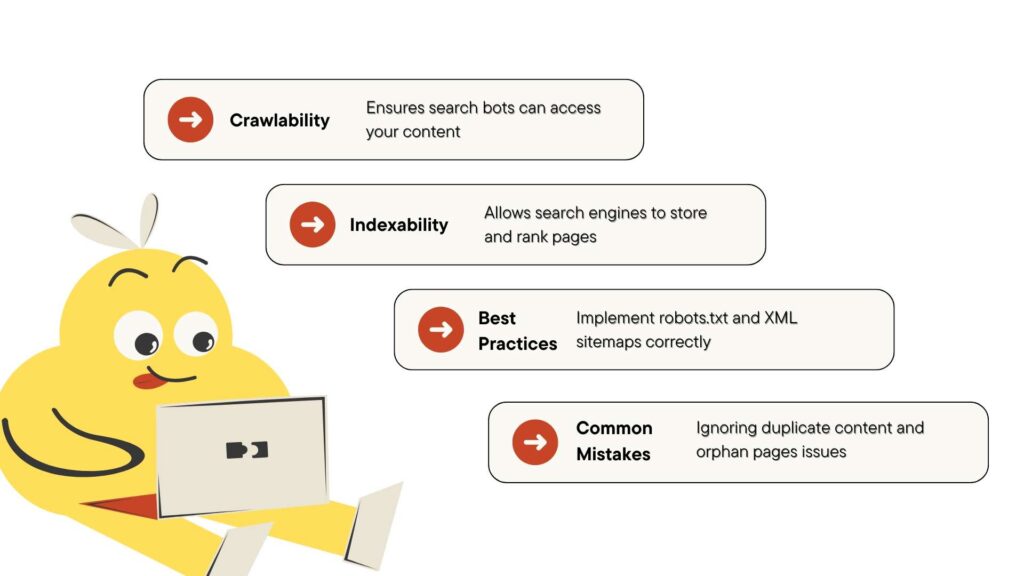
Ensuring Crawlability and Indexability
There is no point in your amazing content not making it to the results pages. This happens when search engines can’t crawl and index your site correctly.
SEO builds on crawlability and indexability. However, most of the time, they get overlooked. It happened more on SaaS websites. They give more priority to product development than technical optimization.
Optimizing Robots.txt and Meta Tags
Robots.txt Best Practices:
- Use robots.txt to manage crawler traffic.
- Allow access to important folders like /blog/, /features/, and /pricing/.
- Disallow private or thin content, such as /admin/, /cart/, or staging areas.
- Avoid blocking essential resources. Some sites mistakenly block / entirely, preventing any crawling.
- Place the robots.txt in the root of your domain.
- Test your robots.txt file using tools like Google Search Console before deploying changes.
- Update the robots.txt file to reflect site structure changes.
Meta Tag Optimization:
- noindex: Use for thank-you pages, admin panels, or internal tools not meant for public search. It instructs search engines not to index a page, excluding it from results while allowing crawler access.
- nofollow: Apply with caution. You can use the nofollow meta tag to stop giving link authority to untrusted or paid links. It saves your crawl budget by preventing bots from following links on less important pages.
- noarchive: Prevents cached versions of your page from being shown. Only use if privacy is a concern. Google has stopped supporting this tag, so it doesn’t really work that well anymore.
Implementing XML Sitemaps
Why sitemaps matter:
They help search engines discover and understand your content. It reaches the dynamic pages or those buried deep in your site structure.
Best Practices:
- Create separate sitemaps for:
- Blog posts
- Product pages
- Documentation
- Landing pages
- Ensure your sitemap:
- Only includes canonical URLs
- Updates automatically when new content is published
- Submitted to Google Search Console.
Many SaaS brands forget to update their sitemaps after redesigns or product launches. This way, their content goes invisible to crawlers.
Handling Orphan Pages and Duplicate Content
Orphan Pages:
These are pages not linked to any other page on your site. Crawlers (and users) can’t find them. This means poor discoverability and indexing by search engines.
How to fix them:
- Use tools like Screaming Frog or Semrush to detect them.
- Interlink from relevant pages (e.g., blog posts linking to product pages).
- Add them to your sitemap if they’re essential and still live.
Duplicate Content:
This confuses search engines and dilutes your ranking potential.
How to handle it:
- Use canonical tags to signal the preferred version of a page.
- Avoid similar content on multiple pages unless necessary.
- Consolidate pages that serve the same intent.
- Use only canonical URLs in XML sitemaps.
- Combine canonical tags with various SEO strategies.
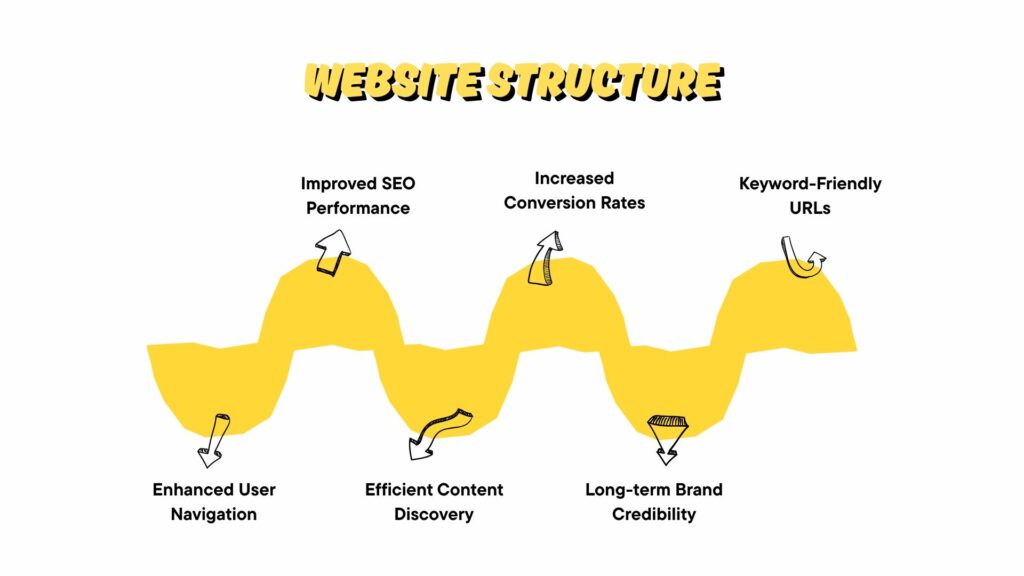
Structuring Your SaaS Website for Optimal SEO
The way your website is structured has a great impact on how easily search engines. It lets users navigate and understand it.
For SaaS companies, which usually have pages for features, pricing plans, documentation, and blog posts, getting this right is super important.
It can be the difference between showing up on the first page of search results or being totally overlooked.
Designing a Logical URL Structure
Your URL structure should be flat, intuitive, and scalable. That means:
- Flat hierarchy: Keep important pages as close to the root domain as possible.
- Example: /features/automation instead of /product/tools/features/automation
- Consistent naming conventions: Use hyphens and lowercase letters, and avoid unnecessary parameters.
- Keyword-friendly: Incorporate relevant keywords naturally.
- Example: /pricing is better than /plans2025.html
Why this matters:
A clean URL structure improves crawlability, indexing speed, and click-through rates. It also makes your site easier for users and search engines alike to navigate.
Internal Linking Strategies
Many SaaS sites neglect internal linking. They are missing an opportunity to strengthen SEO internally.
What works:
- Breadcrumb navigation:
- Enhances user backtracking and search engines’ contextual understanding.
- Example: Home > Features > Automation Tools
- Contextual links in content:
- Link to related blog posts, feature pages, or support docs within the body of your content.
- Use descriptive anchor text like “learn more about automation” instead of “click here”.
- Link from high-authority pages to new or underperforming ones to pass link equity.
Optimizing Category and Tag Pages
These pages often go unnoticed, but they can either boost your SEO or drag it down.
Common issues:
- Thin or duplicate content
- Poor metadata
- Auto-generated, non-optimized lists
How to fix and leverage them:
- Add introductory content to explain the purpose of the category/tag.
- Use unique meta titles and descriptions for each.
- Group content that genuinely shares a common theme.
- Ensure category pages are indexable and included in internal linking.
Enhancing Site Performance and Core Web Vitals
Performance isn’t just about speed; it’s a ranking factor.
Google’s Core Web Vitals measure how real users experience your site. This goes without saying: SaaS brands need speed and smooth functionality.
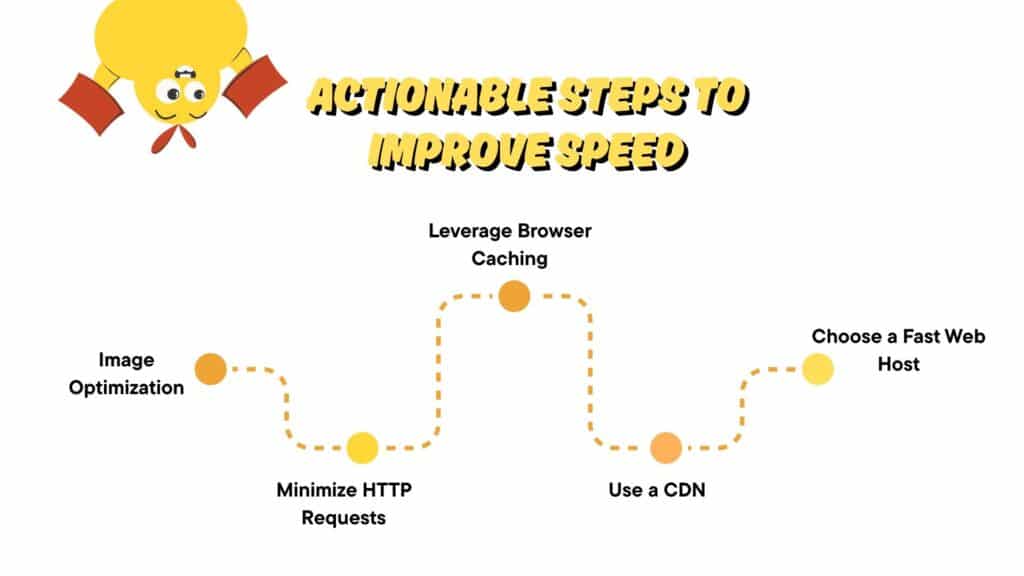
Improving Page Load Speed
Fast-loading pages reduce bounce rates, boost conversions, and help with SEO.
Here’s how to get there:
Key techniques:
- Image optimization
- Use modern formats like WebP/JPEG
- Use tools like TinyPNG, Kraken.io, Squoosh, and Photopea for image compression.
- Set appropriate image dimensions and lazy-load offscreen images
- Minimize HTTP requests
- Combine CSS and JS files where possible
- Avoid unnecessary plugins and scripts
- Fewer HTTP requests limit server connection overhead
- Use inline SVGs instead of loading icon libraries
- Leverage browser caching
- Store static assets locally on users’ browsers for faster repeat visits
- Set proper caching policies
- Store static resources (images, CSS, JavaScript) in visitors’ browsers.
- Set caching rules for images, fonts, and scripts in the .htaccess or server config.
- Use a content delivery network (CDN)
- Serve assets from edge locations closest to the user
- Reduces latency and speeds up loading globally
- Choose a reliable web host with fast server response times
Optimizing for Mobile Devices
More than half of all web traffic now comes from mobile. You’re losing leads because your SaaS site doesn’t work seamlessly across screen sizes.
Mobile performance checklist:
- Responsive design
- Your site should adapt gracefully to various screen sizes and resolutions.
- Use flexible grids and scalable images
- Avoid intrusive elements
- Avoid heavy or problematic elements
- No popups that block content
- Keep CTAs visible and easy to tap
- Include a prominently placed search feature
- Readable content and buttons
- Use legible font sizes
- Ensure buttons have adequate spacing to prevent tap errors
- Optimizing performance from the outset
- Test across devices
- Don’t just rely on simulators
- Check your site on real mobile phones and tablets
- Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test and other similar tools
Monitoring Core Web Vitals
Google’s Core Web Vitals measure three key aspects of user experience:
| Method | Goal | What Happens |
| LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) | Under 2.5 seconds |
|
| FID (First Input Delay) | Under 100 ms |
|
| CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) | Less than 0.1 |
|
Tools to track performance:
- Google PageSpeed Insights
- Lighthouse
- Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX)
- Search Console’s Core Web Vitals report
Implementing Structured Data for Rich Snippets
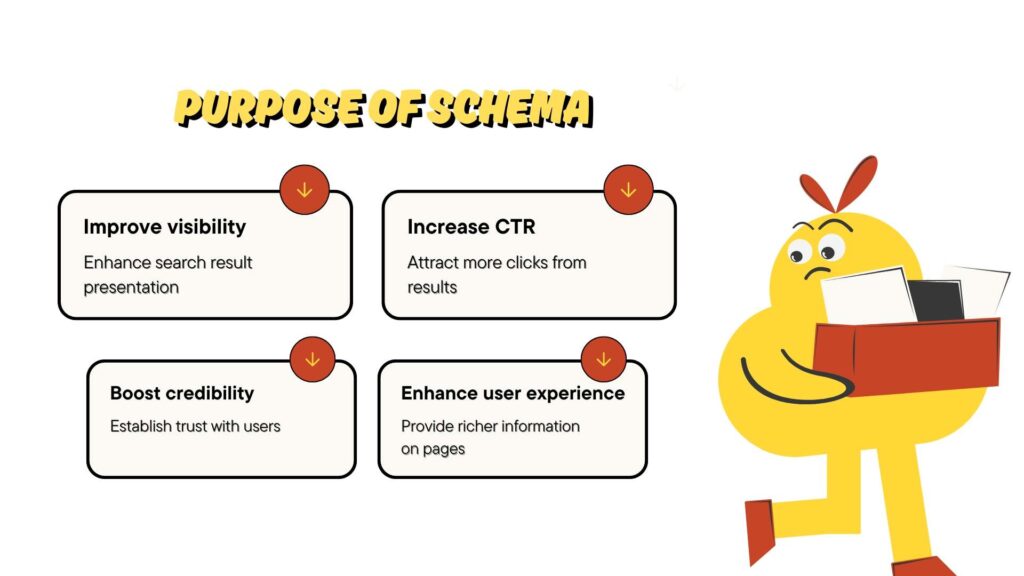
Structured data is like a special sauce that helps search engines understand your content. It can really boost how your pages show up in search results.
For SaaS websites, where competition is high, adding schema markup can make a significant difference.
Understanding Schema Markup
Schema markup is a form of structured data written in JSON-LD (mostly). It tells search engines exactly what each element on your page means, not just what it says. SaaS companies should use it to stand out in competitive search environments.
Most relevant schema types for SaaS:
- Organization
- Displays your company’s name, logo, contact info, and social links in knowledge panels
- Helps build brand authority in search results
- Product
- Perfect for SaaS tools with feature pages or pricing plans
- Shows product name, description, pricing, and sometimes software category
- FAQ
- Allows you to show expandable FAQs directly in search results
- Increases SERP real estate and gives users quick answers before clicking
- Addresses common queries upfront and boosts CTR.
- Review
- Showcases user reviews and ratings for your product
- Adds visual trust signals that can improve CTR and conversions
Tools for Testing and Validation
Even the best schema implementation can fall flat if it’s not error-free. Always test your markup to ensure Google can interpret it correctly.
Recommended tools:
- Rich Results Test (Google)
- Checks whether your structured data is eligible for rich results
- Great for previewing FAQs, reviews, or product info in search
- Schema Markup Validator
- Validates JSON-LD, RDFa, and Microdata formats
- Highlights missing or incorrect fields with helpful debugging
- Google Search Console
- Monitors structured data across your site and flags issues over time
- Use the “Enhancements” tab to view recognized schema types.
Managing JavaScript and Single-Page Applications (SPAs) for SEO in SaaS
SaaS websites are built with JavaScript frameworks (like React, Angular, or Vue) and SPAs. These offer smooth user experiences, but they often frustrate search engines.
Here is how to manage the crawl budget to index dynamic content effectively.
Managing Crawl Budget in JavaScript-Heavy SaaS Apps
What Is Crawl Budget?
The crawl budget is the number of pages Googlebot is willing and able to crawl on your site within a given timeframe. It’s limited, especially for large or complex SaaS sites.
How JavaScript Affects Crawling
JavaScript delays rendering. Googlebot must crawl and then render JS before it can index. This extra step can lead to delays or skipped pages, especially on SPAs.
Diagnosing Crawl Waste in SaaS
Look for:
- Crawled but not indexed pages
- Multiple URLs with minimal content differences (caused by JS routing)
- Repetitive or useless URLs (like filter parameters or session IDs)
- Duplicate content, redirect chains, broken links, or slow-loading pages
Crawl Budget Optimization Techniques
- Block low-value pages via robots.txt
- Use canonical tags to consolidate similar URLs
- Pre-render or use server-side rendering (SSR) for important content
- Minimize unnecessary JS-based navigation
- Keep XML sitemaps clean and updated with canonical URLs
- Minimize redirects and fix broken links
- Adjust settings in GSC if needed
- Link orphan pages to the main site
Tools:
- Google Search Console (GSC): See crawl stats and index coverage
- Log file analysis tools (e.g., Screaming Frog Log Analyzer): Understand what bots are crawling vs. ignoring
Optimizing SaaS SPAs for Indexation
Why SPAs Pose Indexation Issues
SPAs load content dynamically via JavaScript. If content isn’t rendered in the initial HTML, search engines may miss it. It will basically mess with crawler access and indexing.
Search Engine Rendering Limits
Google uses a two-phase crawl:
- Initial HTML
- Deferred JS rendering (can take days or never happen)
Other search engines may not render JS well at all.
SSR vs CSR vs SSG
- CSR (Client-Side Rendering): JS renders content in the browser, which is unsuitable for SEO.
- SSR (Server-Side Rendering): Content is rendered on the server and sent fully formed to crawlers.
- SSG (Static Site Generation): Pages are prebuilt at deployment time. Fastest and most SEO-stable.
Google’s Recommendations
- Use SSR or hybrid rendering (e.g., Next.js, Nuxt.js)
- Use the rendering report in GSC to test how Google sees your content
- Don’t hide content behind user interactions (e.g., tabs or modals)
- Monitor crawl stats and fix server errors promptly
Tools & Implementation Steps
- Use Search Console’s URL Inspection to test real-time rendering
- Use Rendertron, Prerender.io, or built-in SSR from modern frameworks
- Use tools like Lighthouse or Puppeteer to audit JavaScript rendering performance.
- Optimize site speed, reduce JavaScript, and manage internal links
Conducting Technical SEO Audits
Technical SEO supports all other efforts. If it’s broken, even the best content won’t rank. This is why an audit is needed. It will ensure your SaaS website is crawlable, indexable, fast, and user-friendly.
Here’s how to do it right.
Utilizing SEO Audit Tools
The right tools bring the hidden technical issues to the forefront.
Top choices:
- Screaming Frog:
- Crawls your site like Googlebot
- Identifying broken links
- Duplicate content
- Missing tags
- Crawlability issues
- Redirect chains
- Server errors
- Sitebulb:
- Offers in-depth visual reports
- Prioritizes issues by severity
- Great for audits that need stakeholder-friendly insights
- Identify structural, content, and indexing issues.
Other useful options:
- Ahrefs (for backlink and crawl data)
- Google Search Console (indexing, Core Web Vitals, and more)
- GTmetrix (for performance insights)
Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular checkups help you stay ahead of problems.
Best practices:
- Schedule monthly or quarterly audits
- Monitor crawl stats, indexing trends, and broken links in Search Console
- Revalidate structured data and Core Web Vitals periodically
- Keep XML sitemaps updated automatically
Leveraging Advanced Techniques and Emerging Trends
Staying ahead in SaaS SEO means adapting to new formats and search behaviors. Here’s what’s trending:
Voice Search Optimization
Voice queries are typically longer, more conversational, and question-based.
Optimize for:
- Natural language phrasing
- FAQ sections on feature and support pages
- Featured snippet targeting using concise answers
How to optimize:
- Host on YouTube or use embedded players with schema markup
- Add VideoObject structured data
- Include transcripts and captions
- Create landing pages for demo videos with optimized titles and metadata.
AI and Machine Learning in SEO
AI tools are shaping modern SEO workflows. They’re making everything easier, from analyzing data to creating new content.
Use AI for:
- Keyword clustering and topical gap analysis (tools: Surfer, MarketMuse)
- Content briefs and outlines based on SERP data
- Predictive analytics for rankings and competitor trends
- Automating internal linking suggestions at scale
MonsterClaw: Helping SaaS Companies Master Technical SEO
MonsterClaw offers more than just standard SEO. Our approach is data-driven, highly technical, and personalized to each stage of the buyer’s journey. Our team blends technical expertise with deep content strategy.
Core Strengths of MonsterClaw’s SEO Services
- 10-step SEO audit to resolve critical issues
- Comprehensive technical fixes
- Structured data and keyword mapping
- $22M+ in revenue generated for clients
- 3.7M+ organic traffic driven
- Combines SEO with neuro-marketing techniques
- Strong focus on conversion-driven SEO, not just traffic numbers
- Full on-page optimization
- Strong off-page SEO
If your business needs deep technical SEO along with a smart approach that focuses on conversions, MonsterClaw is a great option.
Frequently Asked Questions: Technical SEO for SaaS
How to do SEO for SaaS?
Focus on technical SEO, keyword mapping, creating helpful content, and building backlinks.
What is the difference between SaaS SEO and traditional SEO?
SaaS SEO pursues long-term subscription growth through high-intent, bottom-funnel keywords, while traditional SEO targets one-time sales or local visibility.
What does SaaS mean by SEO?
SaaS SEO focuses on optimizing search engines for Software-as-a-Service companies to increase recurring revenue and attract users organically.
How do I run an ADS in SaaS?
Use platforms like Google Ads or LinkedIn to target decision-makers.